mmHvital: A Study on Head-Mounted mmWave Radar for Vital Sign Monitoring [paper]
As wearable sensing evolves toward non-contact and mobility-friendly designs, mmHvital explores how head-mounted mmWave radar can monitor vital signs such as heart rate (HR) and respiration rate (RR) without chest-level placement. The motivation stems from the limitations of traditional radar setups, which require fixed, front-facing positioning and make them unsuitable for natural, mobile usage in daily scenarios.
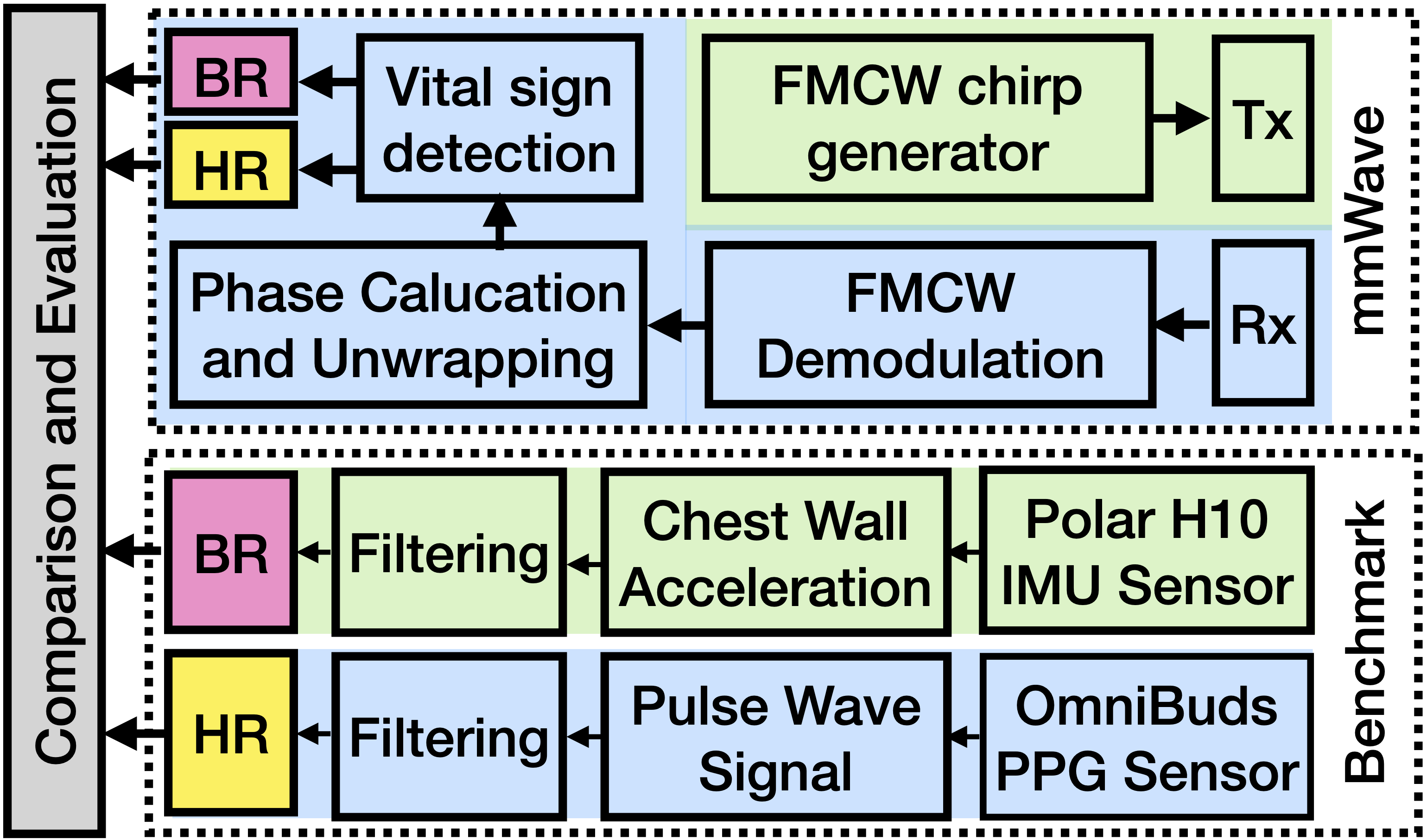
In this work, I designed and built the first head-mounted mmWave sensing prototype for vital sign monitoring, integrating a TI IWR6843AOP radar into a helmet alongside OmniBuds and Polar H10 sensors for benchmarking.
The system investigates how sensor position, user posture, and chest motion visibility affect radar-based HR and RR estimation. To move beyond accuracy-only metrics, I introduced VITAL-KL, a new waveform-similarity metric that quantifies differences in respiratory and cardiac signal morphology between modalities. Results show that front-facing placements achieve high similarity and up to 97% HR accuracy, while rear placements degrade performance due to motion obstruction, which provide design insights for future wearable radar systems, highlighting the feasibility of embedding mmWave sensing into natural form factors such as helmets, glasses, and AR headsets.