Battery-free Wireless Sensor Nodes for Raido and Acoustics Backscatter Communications [paper]
I led a project on battery-free wireless sensor nodes for backscatter communications. The proposed node harvests energy from RF signals at RFID frequency bands, and then reflects the RF signals embedded with the raw signals from analog sensors, e.g., nanogenerators, microphones and piezo sensors. The node enables microwatt-level uplink and downlink communications to an RFID Reader at a distance of a couple of meters.
As an example of application scenarios, the battery-free nodes are deployed in hazardous environments, .e.g, caves, forests and oceans. A low-altitude drone equipped with an RFID Reader collects the data from the nodes by flying along the nodes one by one. The battery-free design in wireless sensor networks improves the scalability and lifetime of wireless sensor nodes by removing the cost of battery maintenance.
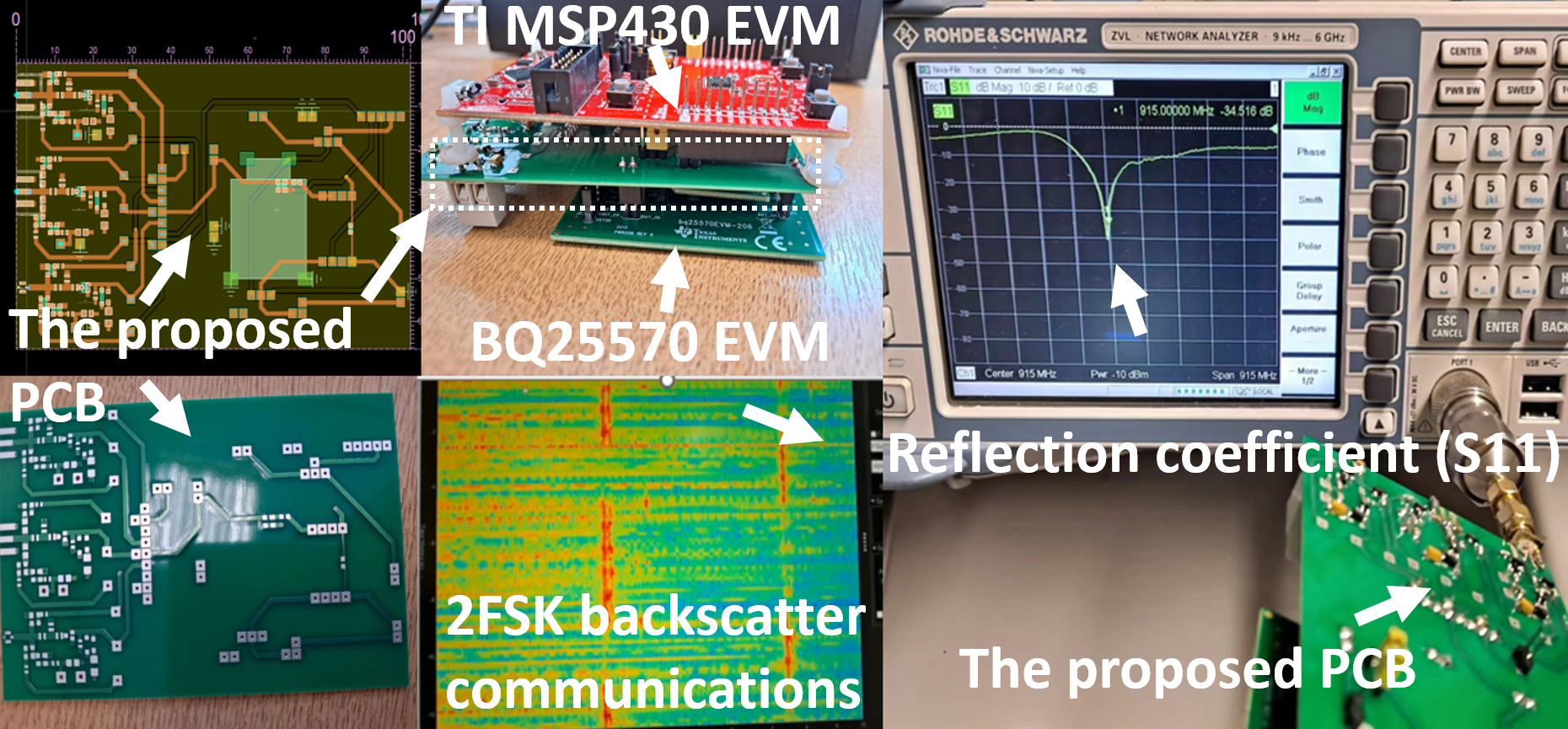
The figures below show the PCB and node design, S11 and the received spectrums of the 2-FSK signals in backscatter communications. The reflection coefficient from the proposed circuit (S11) in the first figure is measured by a Rohde & Schwarz network analyzer, which indicates the circuit has good impedance matching at the target frequency (915 MHz). In this project, Keysight ADS is used for impedance matching, schematic and PCB design, and the Large-Signal S-Parameters (LSSP) and harmonic balance simulation. Ettus USRP is used to evaluate the system’s performance. An ultra-low power chip (TI MSP430) supports power management in energy harvesting and wireless modulation and demodulation in backscatter communications.
 Battery-free Wireless Sensor Node Design and Test |  PCB Design and Assembly |
